Data is growing at a pace that organizations can barely keep up with. Every day, companies generate and store massive volumes of information: emails, contracts, records, and cloud-based files. Without the right framework in place, this data quickly turns from a valuable asset into a major liability.
This is where information governance comes into play. A strong governance strategy reduces risks like data breaches, privacy violations, and regulatory fines, while ensuring information delivers real business value. One of the most widely recognized frameworks for achieving this is the Information Governance Reference Model (IGRM).
In this blog, we’ll unpack the IGRM model, explore its core elements, and explain how it supports a stronger information governance framework that organizations can rely on.
What is IGRM?
The Information Governance Reference Model (IGRM) is a widely recognized information governance framework developed by EDRM.net – the same organization behind the Electronic Discovery Reference Model (EDRM) used across the legal and eDiscovery space.
At its core, the IGRM model serves as a visual and practical guide for organizations, industry associations, and analysts. It helps educate stakeholders about their roles, responsibilities, and dependencies when managing information. More importantly, the framework emphasizes defensible disposition, compliance, and the need for cross-functional collaboration to ensure information is treated as both a valuable asset and a potential risk.
The current version of the IGRM was shaped through extensive industry input. EDRM gathered insights from professionals in records and information management (RIM), legal, compliance, and IT, along with contributions from hundreds of practitioners within the Corporate Governance and Oversight Council (CGOC).
The result is a model designed not just for theory but for real-world application, helping organizations strengthen their information governance practices and align with regulatory demands.
Elements of the IGRM
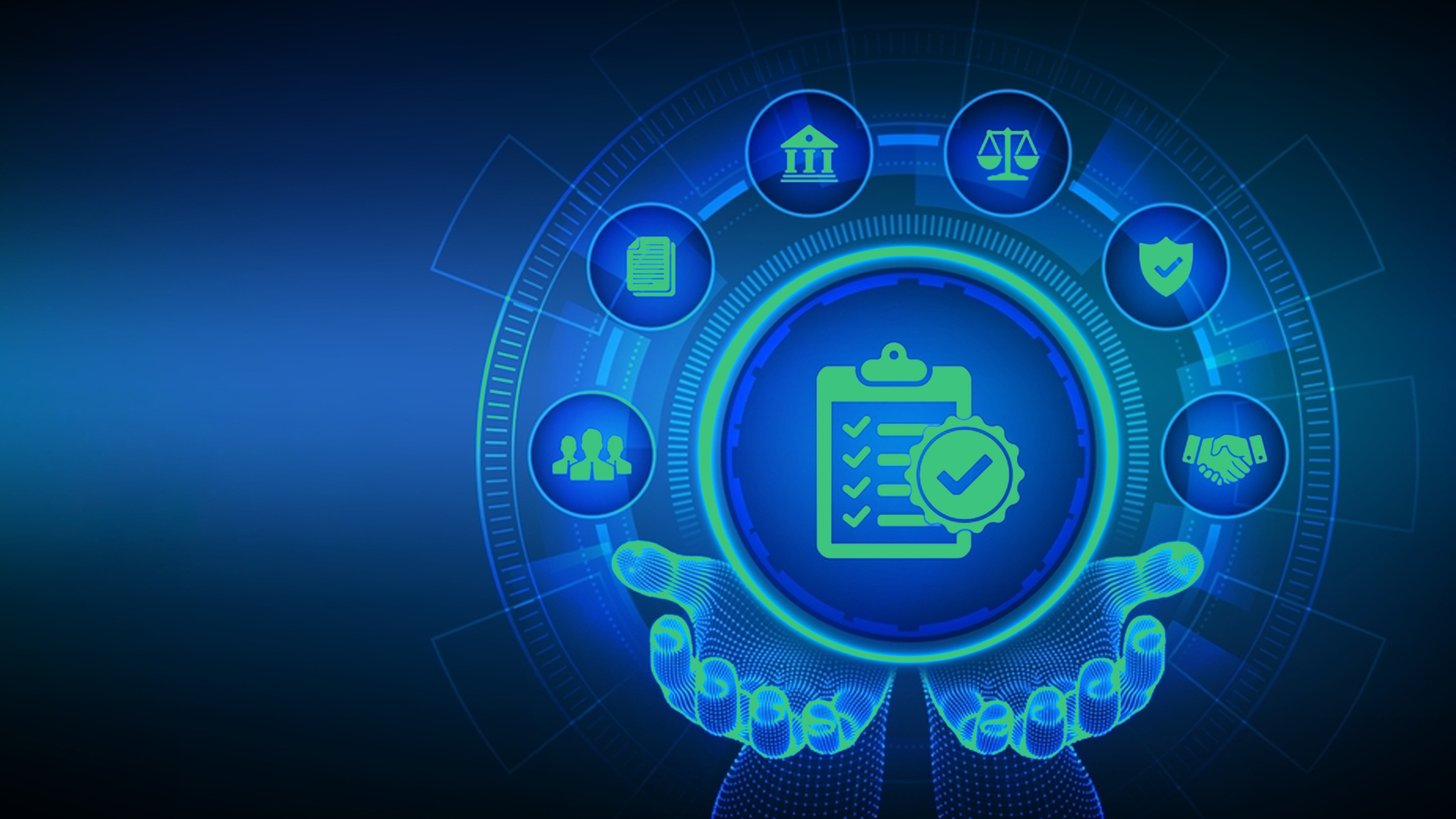
The IGRM model provides a clear visualization of the key components of information governance framework, helping organizations align strategy, compliance, and operations around the data lifecycle.
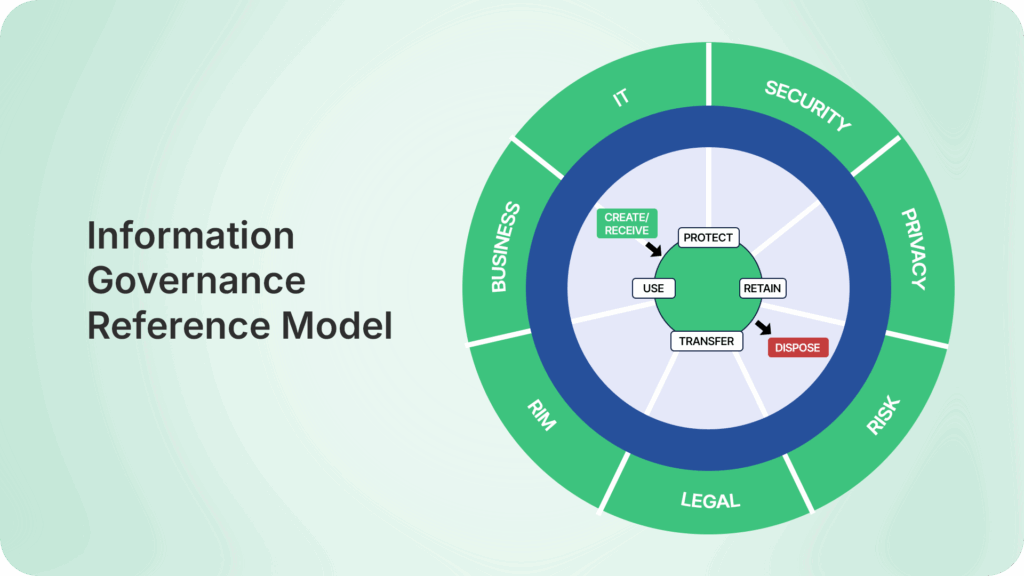
At its core, the model illustrates the information lifecycle: from creation and active use, through retention and archiving, to eventual defensible disposition. This lifecycle sits at the center of the IGRM, encircled by its primary stakeholders:
- Business users – who rely on information for decision-making and assign its value.
- Legal, Risk, and Regulatory teams – tasked with compliance, preservation, and defensibility.
- IT and Security departments – responsible for enabling secure storage, access, and enforcement of data policies.
The Outer Ring
The surrounding outer ring reflects the broader ecosystem that governs data management:
- Business objectives that define information’s value.
- Regulatory and legal obligations that dictate compliance requirements.
- Technology infrastructure that supports policy enforcement and secure collaboration.
What’s New in IGRM 4.1
The latest version of the IGRM model (4.1) highlights the growing importance of privacy as a distinct stakeholder. With increasing global regulations like GDPR and state-level privacy laws, privacy is no longer implied, it’s now explicitly recognized as a core element of information governance.
This evolution underscores a critical reality: information is not only a business asset but also a risk vector. By acknowledging privacy and security as equal partners in governance, the IGRM reflects the modern challenges organizations face in balancing data value with accountability.
In short, the core elements of information governance within the IGRM create a shared framework for aligning value, duty, and infrastructure ensuring that all stakeholders collaborate to manage information consistently and defensibly.
Why Does IGRM Matters?
The IGRM model isn’t just another diagram, it’s a catalyst for true cross-functional collaboration. By clearly illustrating how value and obligation intersect with information assets, it encourages executive dialogue across Legal, IT, Business, RIM, and Privacy teams. EDRM emphasizes how this transparency helps enable defensible disposition and efficient governance across complex environments.
Importantly, the IGRM wasn’t created in isolation; it was shaped by real-world challenges and practitioner feedback. A survey by EDRM and CGOC found that 100% of respondents agreed “defensible disposal” is the main goal of information governance, yet 80% said existing governance models failed to link obligations and information value. That gap is precisely what the information governance framework of IGRM addresses.
In short, the benefits of information governance via the IGRM include:
- Breaking down silos and aligning stakeholders.
- Balancing information’s business value with its legal duty.
- Enabling defensible, cost-effective disposal with reduced risk.
How to Use the IGRM Model?
At first glance, the IGRM model may look like a complex diagram. But its real power lies in how simply it clarifies the core elements of information governance, showing where value, duty, and risk converge around data. It acts as a shared map for stakeholders across Legal, IT, Business, Records & Information Management (RIM), Security, and Privacy, ensuring everyone understands their role in governing information.
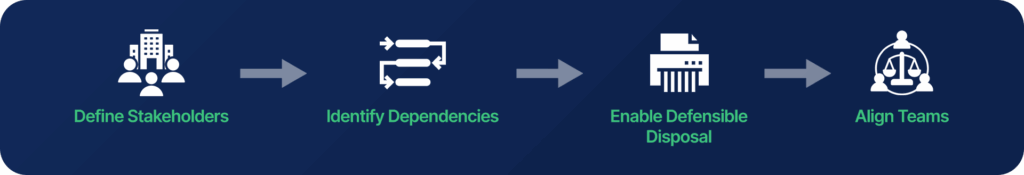
According to EDRM, the framework is designed to do more than educate, it enables actionable collaboration. Organizations can use the information governance framework to:
- Define key stakeholders and establish accountability for data management.
- Identify dependencies between business needs, compliance obligations, and IT controls.
- Support defensible disposition by showing how and when information can be retained, archived, or securely disposed of.
- Align cross-functional teams to improve efficiency and reduce risks.
In practice, the IGRM makes it easier for organizations to design governance policies that balance business value, compliance requirements, and cost control. Rather than leaving governance as a back-office IT task, it turns it into a strategic business function that directly supports operational success.
How Does the IGRM Aligns with the EDRM
The Information Governance Reference Model (IGRM) and the Electronic Discovery Reference Model (EDRM) are closely connected. While the EDRM outlines the nine stages of the eDiscovery lifecycle – from information governance through presentation – the IGRM goes deeper into the key components of an information governance framework that underpin the very first step.
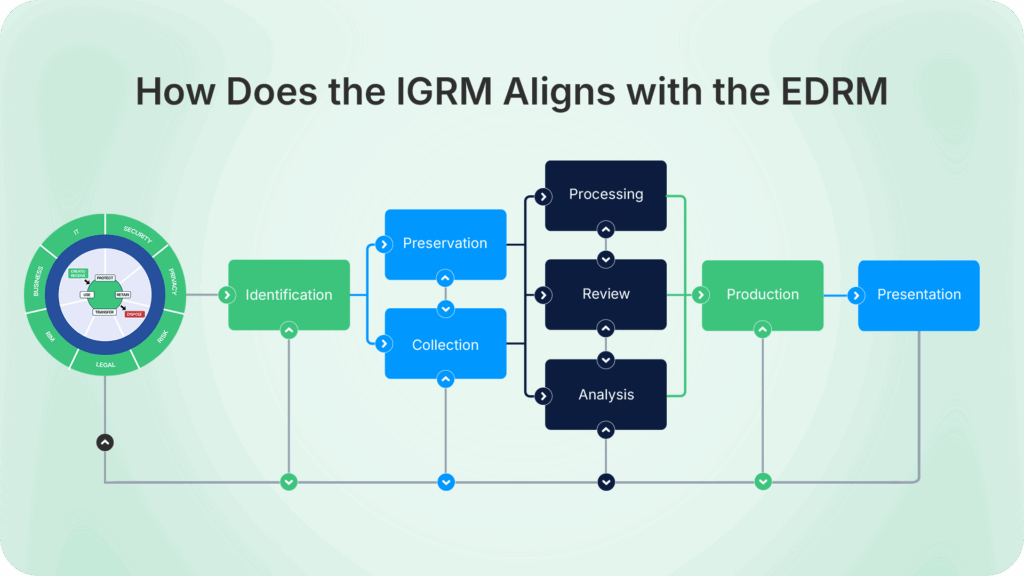
Simply put, the IGRM sets the foundation for effective eDiscovery by clarifying who owns data, how it should be managed, and when it can be defensibly disposed of. Without strong governance, the later stages of the EDRM model like: identification, preservation, and review become more complex, costly, and risky.
By aligning the two models, organizations gain a holistic view:
- IGRM defines the core elements of information governance, stakeholder responsibilities, and data dependencies.
- EDRM operationalizes those principles across the discovery process, ensuring compliance, defensibility, and efficiency.
Together, the IGRM and EDRM create a unified roadmap for both information governance and eDiscovery, bridging strategy with execution.
How Does the IGRM Help
The Information Governance Reference Model (IGRM) is more than a framework, it’s a practical guide for organizations to improve the way they manage information. By clearly defining the core elements of information governance and mapping stakeholder responsibilities, the model helps reduce risks, streamline processes, and maximize the value of data.

The benefits of information governance with the IGRM include:
- Stronger collaboration across departments – Legal, IT, compliance, records management, and business teams gain a shared understanding of their roles and dependencies.
- Reduced legal and regulatory risks – By clarifying retention, privacy, and disposal rules, organizations stay compliant with evolving laws and minimize costly errors.
- Improved efficiency and cost control – Well-governed data is easier to locate, manage, and use, cutting down discovery costs and response times.
- Enhanced data value – Information is not only secured but also made more accessible to support business insights and decision-making.
In short, the IGRM model helps organizations turn information governance from a siloed obligation into a cross-functional strategy that safeguards data while driving business value.
Transform the Way You Manage Information
Information governance is complex – but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Venio Systems helps Legal, IT, and Compliance teams break down silos, manage data across its lifecycle, and stay defensible in the face of growing regulatory demands.
When it boils down to it, information governance is considerably complex. It impacts all departments and all workflows. Plus, it’s constantly evolving with the ever-changing IT landscape and the acceleration of big data.
With all this in mind, it’s important to view information governance through a wider eDiscovery lens. Ultimately, governance is just one of the many steps that you have to go through when preparing for court, and each stage is equally as important.
At the end of the day, your team has to be able to procure information quickly and efficiently. If you can’t do that, then you risk missing important court deadlines and losing your cases.
Your best bet is to streamline eDiscovery by using a purpose-built platform like Venio Systems. It empowers legal, compliance, and IT teams to break down silos, manage data throughout its lifecycle, and stay defensible in the face of growing regulatory demands.
By aligning with the core elements of information governance, Venio ensures your organization is prepared not just for today’s challenges but also for what’s ahead. Ready to transform your approach to information governance? Contact us today!
FAQs About IGRM
What Are the Core Principles of Information Governance?
The three core principles are accountability, integrity, and transparency. Together, they ensure data is reliable, well-managed, and defensible across its lifecycle.
How Does the IGRM Framework Support Compliance?
The IGRM model aligns stakeholders and processes to meet regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, ensuring defensible data management and audit readiness.
In What Ways Does IGRM Influence Decision-Making?
By linking data value to risk, the IGRM model helps organizations make smarter choices on retention, disposal, and compliance, while improving collaboration across teams.






